Getting Started
Quick Start
Get up and running with the Avocado Linux SDK in minutes.
Prerequisites
- Linux development machine (Ubuntu 22.04+, Fedora 39+)
- Podman or Docker installed
- 20GB+ available disk space
Installing and running the SDK
- Pull the SDK container:
podman pull avocadolinux/sdk:apollo-edge- Create your workspace:
mkdir avocadocd avocado- Start the SDK environment:
podman run -it --rm -e AVOCADO_SDK_TARGET=qemux86-64 -v $(pwd):/opt:z --entrypoint entrypoint.sh avocadolinux/sdk:apollo-edge /bin/bashFor a list of supported Avocado SDK targets besides qemux86-64, return to the Development Environment page.
Perform all remaining exercises from inside the SDK container.
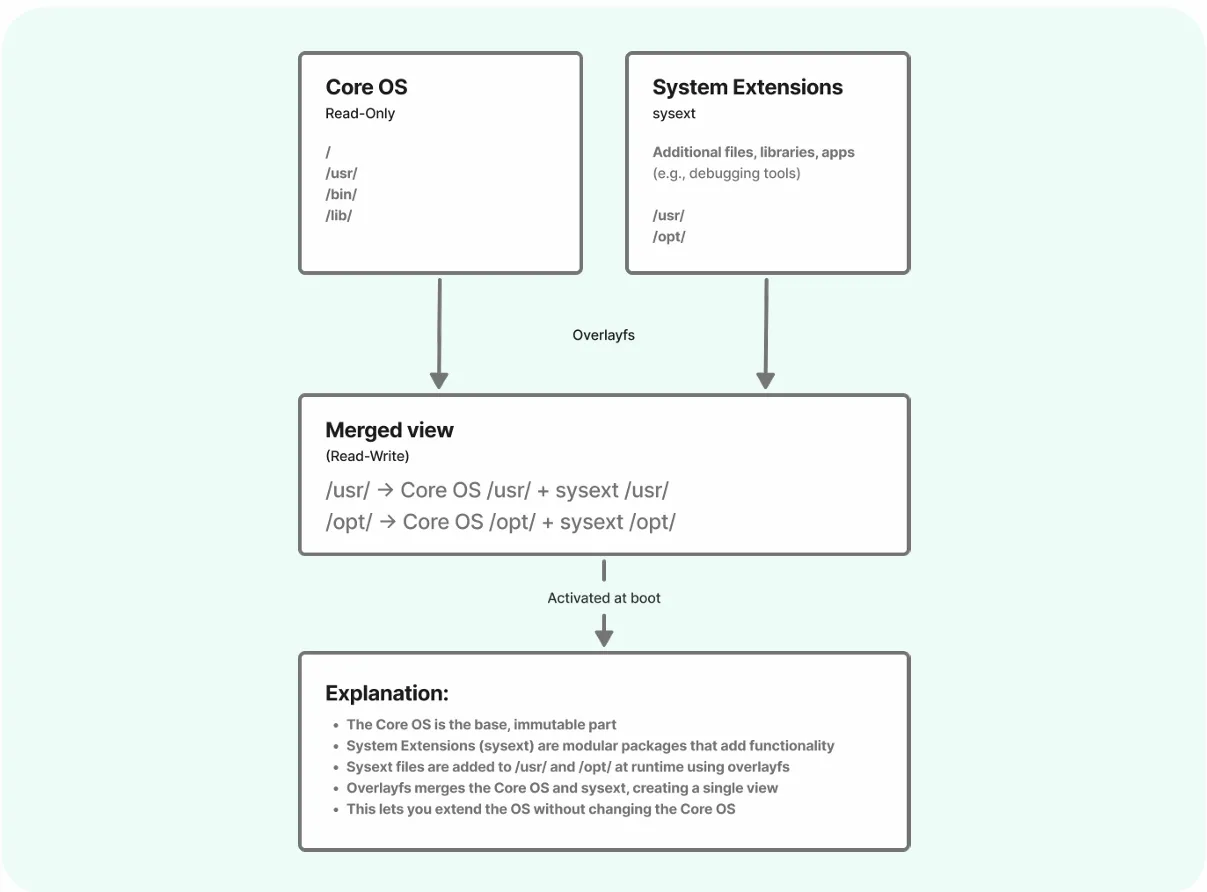
Building a system extension
Let’s build a system extension that adds peridiod to the runtime.
- Install package contents for the peridiod package to the sysext sysroot:
avocado-repo sysext install peridiod -y- Build system extension:
avocado-build sysext peridiod- Verify that a peridiod system extension raw file was output:
ls -l /opt/_avocado/extensions/sysext/peridiod.rawBuilding a bootable image
- Download the necessary images for the bootchain and the core rootfs to use when building a complete system image.
avocado-repo images- Build var partition containing extension contents:
avocado-build var- Build complete system image.
avocado-build image- Verify that a complete system image file was output:
ls -l /opt/_avocado/output/avocado-image-qemu*.imgBooting an image with QEMU
- Extend the toolchain with QEMU:
avocado-repo sdk install nativesdk-qemu- Run the emulator:
avocado-run-qemuThe peridiod system extension should start automatically.
systemd-sysext merge